Working with Python and Matlab
Almost everything I’ve done while at Rice has been in Matlab. It’s very popular in academia, but that’s been threatened by Python for a while with most Data Science applications almost exclusively using it now. The biggest strengths I can think of for Matlab are their toolboxes and the fact that most of the previous code that I’ve written so far was written in Matlab.
However, I’m beginning to realize I may not always have access to a Matlab license. Furthermore, I realize the strengths of Python including the many open source community tools like Read The Docs and TravisCI along with packages like keras for machine learning. To prepare for my eventual Matlabless future, I am converting many of my works to Python and trying to improve my documentation along the way. However, there are still things that are in Matlab, that I can’t easily translate (without lots of work). Most notably are
- WARPLab. This allows me to prototype and test on the WARRP SDR board.
- RFWebLab. This allows me to send signals through a PA set up at Chalmers University for my DPD related work.
To combat this, I am working on a way to have a workaround to allow me to use my new python code with these APIs in Matlab. The rest of this post outlines my procedure to use PyCharm to run Matlab code. This information was all extracted from the official Matlab guides on the topic.
Steps to take in Windows.
Install Python 3.6
(Download)[https://www.python.org/downloads/windows/] and install Python 3.6. Be sure to add it to the path. As of now, Python 3.6 is the latest version that can use the Matlab tools. Make sure you can run python from the Windows PowerShell.
Get the Matlab Root Directory
In Matlab, run
matlabroot
Mine was: C:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2018b
Navigate to that directory in PowerShell
Open PowerShell as an administrator then cd to the root direcory plus extern\engines\python.
cd "C:\Program Files\MATLAB\R2018b\extern\engines\python\"
Install Matlab for Python
python setup.py install
Steps to take in PyCharm
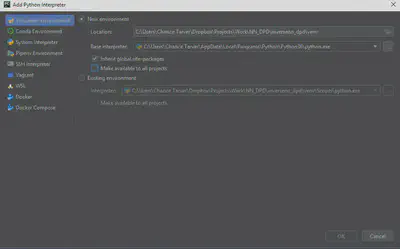
For every project, a virtual environment should be created. When creating your virtualenv, choose yout Python 3.6 as your base interpreter. Select the option to Inherit global site-packages. This will pull in the matlabengineforpython package into the virtualenv.
Code Example.
This is a piece of a project I’m currently working on. In this example, webRF is a Matlab handle object that I use to communicate with RFWebLab.
eng = matlab.engine.start_matlab() # Launch the matlab engine.
board = eng.webRF() # Call the constructor of my class
signal_out = eng.transmit(board, signal_in) # Call method transmit from class webRF.
Sending Data Back and Forth
TO BE UPDATED SOON. Matlab doesn’t like using numpy arrays :(
Future Steps
Investigate using Octave. I still want to use Python as much as possible. But until I get a version of WARPLab written entirely in Python, I’ll need Matlab or an alternative like Octave. I’ll be trying to see if I can run WARPLab and other tools using Octave soon.